Digestive problems & pancreas
It is true that food is a fuel for our bodies – it provides energy and all important nutrients. But it should not definitely be the only reason to eat – food should also be enjoyed! Sharing a meal with your family, friends or colleagues should be a moment to cherish and remember. To do so, we need to digest the food in the right way, requiring a sufficient amount of digestive enzymes.
Why is pancreas so important when it comes to good food?
These enzymes are made in the pancreas. In the old days, people thought the pancreas with its rubbery consistence was only a shock absorber protecting the stomach. But it truly is much more! Thanks to enzymes made by the pancreas, our body is able to break down food into tiny parts that can transfer from the intestine into the bloodstream and travel to tissues and organs.
If there is something wrong with your pancreas, it does not produce enough enzymes. The food is not broken down sufficiently and various digestive problems may occur. When you discuss your digestive problems with your doctor, he may use the term “Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency” which is simply the medical term for the lack of pancreatic enzymes.
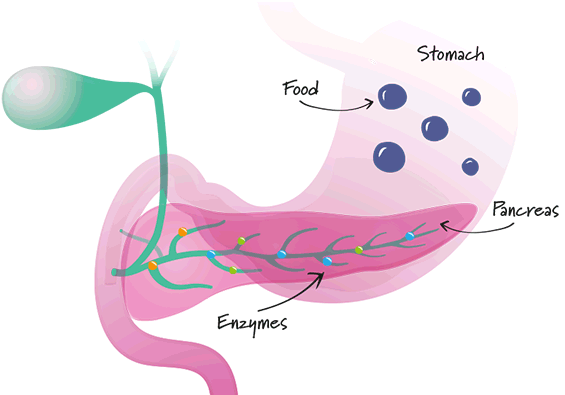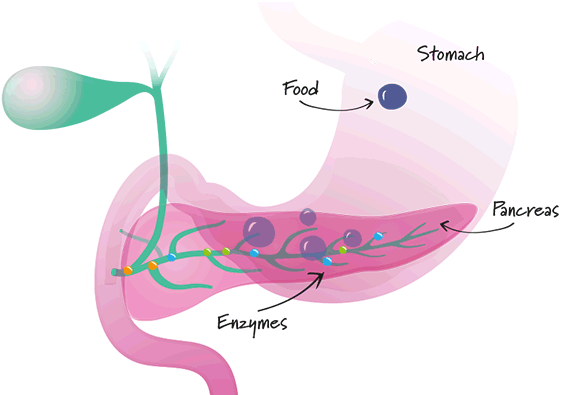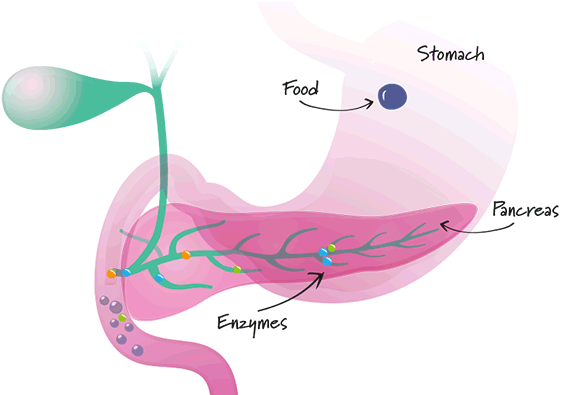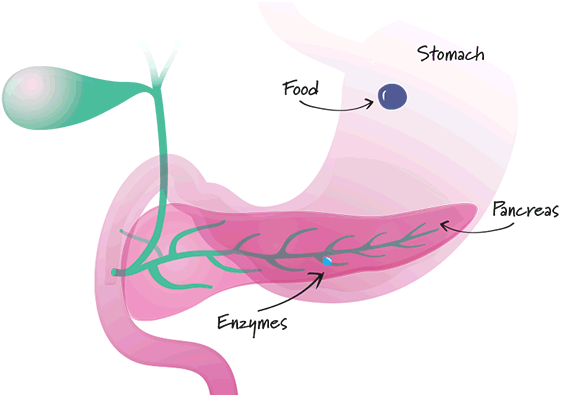
- Healthy pancreas
Digestive enzymes made in the pancreas break down proteins, fats and carbs into smaller particles. - Patient with digestive problems
If there is any disturbance in the pancreas, there is a lack of digestive enzymes and the fats, proteins and carbs are not broken down properly. - Patient taking Mezym
Mezym replaces the lacking enzymes and helps to digest food.
Who can suffer from exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a health condition characterized by the lack of digestive enzymes produced by pancreas and it can affect people of all ages, but the older you are the higher the risk that your digestive problems are related to the pancreas.




Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency symptoms
The symptoms vary from mild and moderate to severe and they include:
Mild symptoms: Discomfort or heavy feeling in the stomach after eating poorly digestible, fatty, spicy or unusual food. *
Moderate symptoms: Dyspeptic symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating or diarrhea. *
Severe symptoms: Chronic abdominal pain, diarrhea and steatorrhea (fat in the stool), weight loss, osteoporosis, etc.*
* Only your doctor can diagnose the exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency and its causes
Have you ever thought that your digestive problems might be related to the function of the pancreas? The medical condition when the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes is called exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Here are some situations as well as medical conditions when the pancreas might not be working as it should:

Age
It is normal that production of digestive enzymes is decreasing with age. The older you are the higher the chance of developing digestive problems associated with the function of your pancreas.

Alcohol consumption and smoking
people that regularly consume alcohol and smoke often suffer from exocrine pancreatic insufficiency associated with chronic pancreatitis.
Diabetes
diabetics can also suffer from exocrine pancreatic insufficiency as both these health issues are related to the pancreas.

After surgery or injury
if part of the pancreas was removed surgically (tumors, after an injury, etc.) its function is usually also affected.

Genetic diseases
for example the most common cause of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in children is cystic fibrosis.


How to live with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency?
The treatment of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency involves using PERT medication (Pancreatic Enzymes Replacement Therapy), normal-nonrestrictive healthy diet and some lifestyle changes. Only the combination of these aspects may help you alleviate your symptoms and enjoy your meals again and live a good life.
Monitor what you eat and how you feel afterwards. Then you will be able to avoid foods that worsen your symptoms.
Strict low-fat diet is no longer recommended to patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. You should avoid fiber-rich foods instead. Fiber is difficult to digest and apart from that it inactivates pancreatic lipase (the digestive enzyme that breaks down fats).
Eat more frequently and smaller portions of high-energy food.
To make sure your diet covers all your nutritional needs and to avoid complications of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency such as malnutrition, lack of vitamins or osteoporosis, consult a nutritionist.
Take PERT with every meal you eat. Before you start using pancreatin (the combination of digestive enzymes) always read carefully the patient information leaflet.
Stop smoking. Do not drink alcohol.
How can MEZYM help you?
You should take Mezym during the meal to replace the pancreatic digestive enzymes. Mezym will help you lighten your stomach after eating.
You should also make some lifestyle changes that mainly involve eating a well-balanced diet covering your individual nutritional needs (with individual tolerance being a significant factor), and avoiding alcohol and tobacco.
Digestive enzymes are substances that break down food into smaller particles and thus enable the body to get all the necessary nutrients.
Pancreatin is a combination of digestive enzymes produced by pancreas.
Lipase is a digestive enzyme that breaks down fats.
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys and intestine.
PERT is a type of medication that is used to replace pancreatic digestive enzymes in case of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Galenic forms are forms in which the drug can be administered (tablets, capsules, suspension etc).
Most of the nutrients in food fall into three major groups: proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Steatorrhea – oily stools due to the reduced absorption of fat by the intestine.
